pyboard快速参考¶
下面的引脚图是 PYBv1.0. pyboard其他版本的见: PYBv1.1 PYBLITEv1.0-AC PYBLITEv1.0.
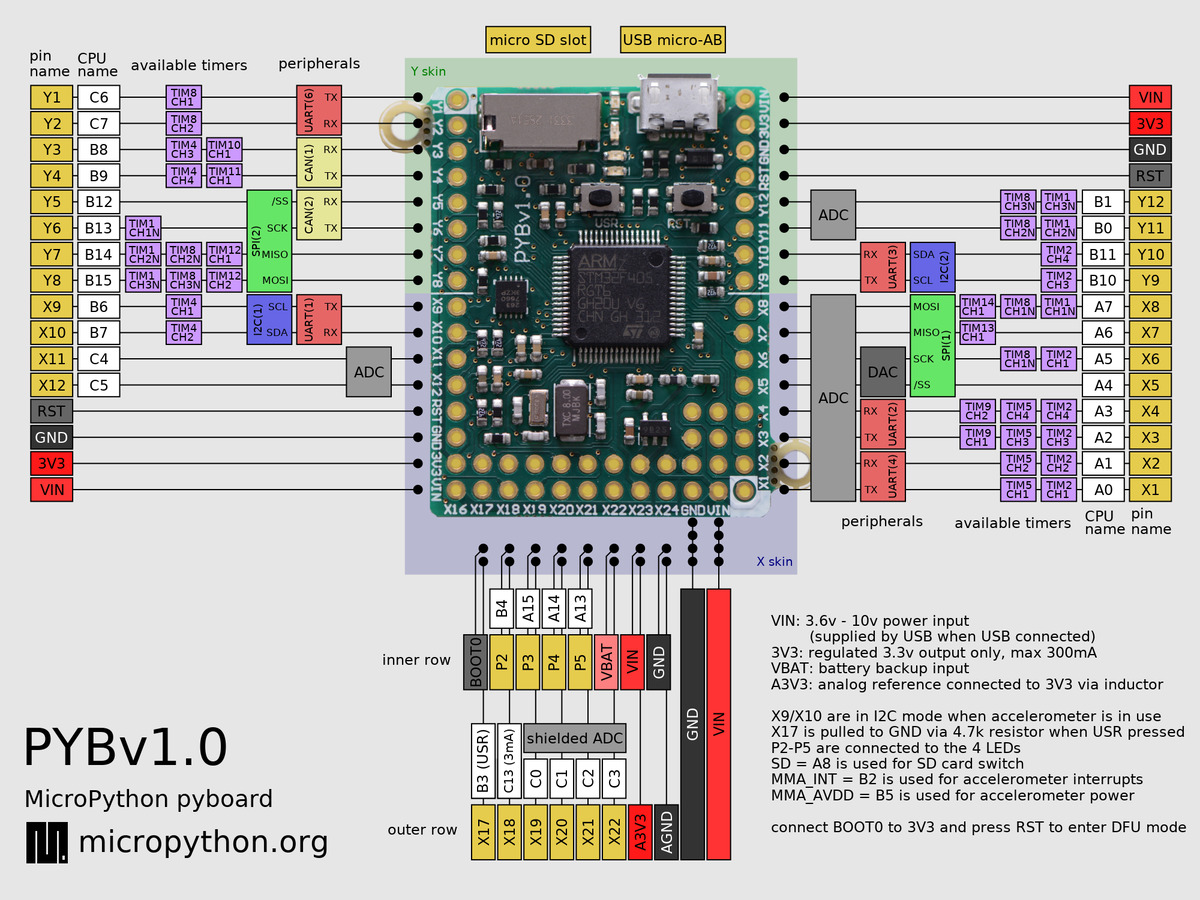
通用硬件控制¶
See pyb.
import pyb
pyb.repl_uart(pyb.UART(1, 9600)) # duplicate REPL on UART(1)在UART(1)上重置REPL
pyb.wfi() # pause CPU, waiting for interrupt 暂停cpu,等待中断
pyb.freq() # get CPU and bus frequencies 获得CPU频率
pyb.freq(60000000) # set CPU freq to 60MHz 设置CPU频率
pyb.stop() # stop CPU, waiting for external interrupt 停止cpu,等待外部中断
延时和时间¶
Use the time module:
import time
time.sleep(1) # sleep for 1 second 延时1s
time.sleep_ms(500) # sleep for 500 milliseconds 延时500ms
time.sleep_us(10) # sleep for 10 microseconds 延时10us
start = time.ticks_ms() # get value of millisecond counter 获取毫秒计数器的值
delta = time.ticks_diff(time.ticks_ms(), start) # compute time difference 计算时间差
Pins and GPIO¶
See pyb.Pin.
from pyb import Pin
p_out = Pin('X1', Pin.OUT_PP)
p_out.high()
p_out.low()
p_in = Pin('X2', Pin.IN, Pin.PULL_UP)
p_in.value() # get value, 0 or 1
舵机控制¶
See pyb.Servo.
from pyb import Servo
s1 = Servo(1) # servo on position 1 (X1, VIN, GND) 位置1的servo(X1)
s1.angle(45) # move to 45 degrees
s1.angle(-60, 1500) # move to -60 degrees in 1500ms 在1500ms内移动到-60度
s1.speed(50) # for continuous rotation servos 连续旋转舵机
外部中断¶
See pyb.ExtInt.
from pyb import Pin, ExtInt
callback = lambda e: print("intr")
ext = ExtInt(Pin('Y1'), ExtInt.IRQ_RISING, Pin.PULL_NONE, callback)
定时器¶
See pyb.Timer.
from pyb import Timer
tim = Timer(1, freq=1000)
tim.counter() # get counter value 获取计时器值
tim.freq(0.5) # 0.5 Hz
tim.callback(lambda t: pyb.LED(1).toggle())
PWM脉宽调制¶
from pyb import Pin, Timer
p = Pin('X1') # X1 has TIM2, CH1
tim = Timer(2, freq=1000)
ch = tim.channel(1, Timer.PWM, pin=p)
ch.pulse_width_percent(50)
ADC (模数转换)¶
from pyb import Pin, ADC
adc = ADC(Pin('X19'))
adc.read() # read value,读取值 0-4095
DAC (数模转换)¶
from pyb import Pin, DAC
dac = DAC(Pin('X5'))
dac.write(120) # 输出介于0-255
UART (串行总线)¶
See pyb.UART.
from pyb import UART
uart = UART(1, 9600)
uart.write('hello')
uart.read(5) # read up to 5 bytes 读取5个字节
SPI总线¶
See pyb.SPI.
from pyb import SPI
spi = SPI(1, SPI.MASTER, baudrate=200000, polarity=1, phase=0)
spi.send('hello')
spi.recv(5) # receive 5 bytes on the bus 在总线上接收5个字节
spi.send_recv('hello') # send and receive 5 bytes 发送5个字节
I2C bus¶
See pyb.I2C.
from pyb import I2C
i2c = I2C(1, I2C.MASTER, baudrate=100000)
i2c.scan() # returns list of slave addresses 返回一个从属设备地址的列表
i2c.send('hello', 0x42) # send 5 bytes to slave with address 0x42 使用0x42地址向从属设备发送5个字节
i2c.recv(5, 0x42) # receive 5 bytes from slave 从从属设备上接收5个字节
i2c.mem_read(2, 0x42, 0x10) # read 2 bytes from slave 0x42, slave memory 0x10 从地址为0x42从属设备上接收2个字节,从属存储器为0x10
i2c.mem_write('xy', 0x42, 0x10) # write 2 bytes to slave 0x42, slave memory 0x10 向地址为0x42的从属设备写入2个字节,从属存储器为0x10